Hand Anatomy
The human hand is made up of the wrist, palm, and fingers and consists of 27 bones, 27 joints, 34 muscles, over 100 ligaments and tendons, and many blood vessels and nerves.
The hands enable us to perform many of our daily activities such as driving, writing and cooking. It is important to understand the normal anatomy of the hand to learn more about diseases and conditions that can affect our hands.
Bones of the Hand
The wrist is comprised of 8 carpal bones. These wrist bones are attached to the radius and ulna of the forearm to form the wrist joint. They connect to 5 metacarpal bones that form the palm of the hand. Each metacarpal bone connects to one finger at a joint called the metacarpophalangeal joint (MCP joint). This joint is commonly referred to as the knuckle joint.
The bones in our fingers and thumb are called phalanges. Each finger has 3 phalanges separated by two interphalangeal joints, except for the thumb, which has only 2 phalanges and one interphalangeal joint.
The first joint close to the knuckle joint is called the proximal interphalangeal joint (PIP joint). The joint closest to the end of the finger is called the distal interphalangeal joint (DIP joint).
The MCP and PIP joint act like hinges when the fingers bend and straighten.
Soft Tissues of the Hand
Our hand bones are held in place and supported by various soft tissues. These include: articular cartilage, ligaments, muscles and tendons.
Articular cartilages are smooth material that act as shock absorbers and cushion the ends of bones at each of the 27 joints, allowing smooth movement of the hand.
Muscles and ligaments function to control the movement of the hand.
Ligaments are tough rope-like tissues that connect bones to other bones, holding them in place and providing stability to the joints. Each finger joint has two collateral ligaments on either side, which prevents the abnormal sideways bending of the joints. The volar plate is the strongest ligament in the hand. It joins the proximal and middle phalanx on the palm side of the joint and prevents backward bending of the PIP joint (hyperextension).
Muscles of the Hand
Muscles are fibrous tissues that help produce movement. They work by contracting.
There are two types of muscles in the hand:
- Intrinsic muscles are small muscles that originate in the wrist and hand. They are responsible for fine motor movements of the fingers during activities such as writing or playing the piano.
- Extrinsic muscles that originate in the forearm or elbow control the movement of the wrist and hand. These muscles are responsible for gross hand movements. They position the wrist and hand while the fingers perform fine motor movements.
Each finger has six muscles controlling its movement: three extrinsic and three intrinsic muscles. The index and little finger each have an extra extrinsic extensor.
Tendons of the Hand
Tendons are soft tissues that connect muscles to bones. When muscles contract, tendons pull the bones, causing the finger to move. The extrinsic muscles are attached to finger bones through long tendons that extend from the forearm through the wrist. Tendons located on the palm side help in bending the fingers and are called flexor tendons, while tendons on top of the hand called extensor tendons help in straightening the fingers.
Nerves of the Hand
Nerves of the hand carry electrical signals from the brain to the muscles in the forearm and hand, enabling movement. They also carry the senses of touch, pain and temperature back from the hands to the brain.
The three main nerves of the hand and wrist include:
- Ulnar nerve: The ulnar nerve crosses the wrist through an area called Guyon’s canal and branches to provide sensation to the little finger and half of the ring finger.
- Median nerve: The median nerve crosses the wrist through a tunnel called the carpal tunnel. The median nerve provides sensation to the palm, thumb, index finger, middle finger and part of the ring finger.
- Radial nerve: The radial nerve runs down the thumb side of the forearm and provides sensation to the back of the hand from the thumb to the middle finger.
All three nerves originate at the shoulder and travel down the arm to the hand. Each of these nerves has sensory and motor components.
Blood Vessels of the Hand
Blood vessels travel beside the nerves to supply blood to the hand. The main arteries are the ulnar and radial arteries, which supply blood to the front of the hand, fingers, and thumb. The ulnar artery travels next to the ulnar nerve through the Guyon’s canal in the wrist. The radial artery is the largest artery of the hand, traveling across the front of the wrist, near the thumb. Pulse is measured at the radial artery.
Other blood vessels travel across the back of the wrist to supply blood to the back of the hand, fingers and thumb.
Bursae of the Hand
Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that decrease friction between tendons and bone or skin. They contain special cells called synovial cells that secrete a lubricating fluid.
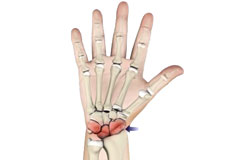
Arthritis of the Hand and Wrist
Arthritis is an inflammatory condition of the joints. There are several types of arthritis and the most common type is osteoarthritis or wear-and-tear arthritis. Arthritis affects various joints in the body and the arthritis in the hand affects the joint at the base of the thumb.
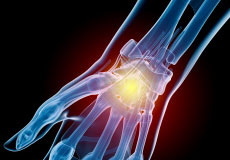
Wrist Injuries
The wrist is a commonly injured joint in the body. Problems include sprains and strains as well as fractures that can occur with lifting and carrying heavy objects, while operating machinery, bracing against a fall, or from sports-related injuries.
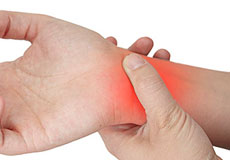
Wrist Pain
Wrist pain is defined as any ache or discomfort in the wrist. The wrist is comprised of two bones in the forearm, the radius and ulna, and eight tiny carpal bones in the palm.
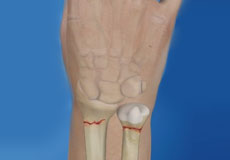
Wrist Fracture
The wrist is comprised of two bones in the forearm, the radius and ulna, and eight tiny carpal bones in the palm. The bones meet to form multiple large and small joints.
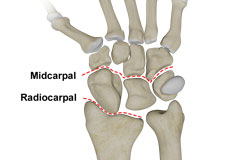
Carpal Instability
Carpal instability is the loss of alignment of the carpal bones and/or radioulnar joint. The wrist is a complex joint that connects the forearm to the hand and allows it to move.
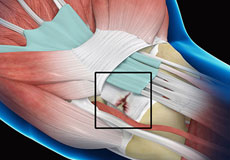
Wrist Ligament Tear and Instability
A ligament is a strong, flexible band of fibrous tissue. The wrist has many ligaments that help to keep the wrist bones in proper position providing stability to the joint.
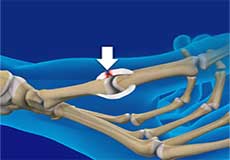
Gamekeeper's Thumb
Gamekeeper's thumb, also known as skier's thumb, is a tear of the ulnar collateral ligament, a band of tissue that supports the joint at the base of the thumb.
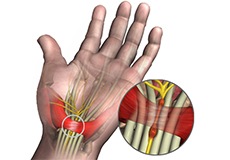
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common, painful, progressive condition that is caused by compression of the median nerve at the wrist area.

Dupuytren's Contracture
Dupuytren’s contracture is a hand condition where thickening of the underlying fibrous tissues of the palm causes the fingers to bend inward. This makes it difficult to fully straighten the affected fingers.

Boutonniere Deformity
Tendons in your fingers connect the finger bones to finger muscles and help bend and straighten the finger at the joint when the muscles contract. Boutonnière deformity is a condition in which a tendon injury to the middle joint of the finger results in the inability to straighten the affected finger.
Hand Infections
Hand infections, if left untreated or treated improperly, can cause disabilities such as stiffness, contracture, weakness, and loss of tissues (skin, nerve and bone) that will persist even after the infection resolves.
De Quervain's Tendinosis
Inflammation and swelling of the tendon sheaths put pressure on the adjacent nerves and leads to pain and numbness in the thumb side of the wrist. Strain on these tendons can cause swelling and irritation, and lead to a condition called De Quervain's tenosynovitis, which is characterized by inflammation.
Wrist Sprains
Injuries caused due to stretching or tearing of the ligaments in the wrist are called wrist sprains. Sprains can range from mild to severe, based on the extent of injury to the ligament.
Kienbock's Disease
Kienbock's disease is a condition in which the lunate, one of the small bones of the wrist loses its blood supply leading to death of the bone. This results in pain, stiffness, and degenerative changes in the wrist joint.
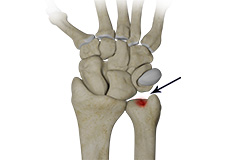
Ulnar Carpal Impaction
The wrist is a complex joint made up of 8 carpal bones aligned in two rows, with four bones present in each row. The carpal bones are further connected to 5 metacarpal bones that form the palm of the hand.
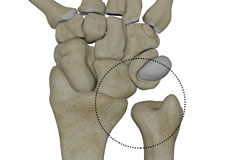
Distal Radioulnar Joint (DRUJ) Instability
Distal radioulnar joint instability is the abnormal orientation or movement of the radius and ulna bones at the wrist in relation to one another. Injury to the tendons, ligaments and/or muscles stabilizing the joint may cause partial or complete dislocation.
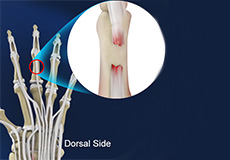
Extensor Tendon Injuries
Tendons are bands of tissue connecting muscles to bones. The extensor tendon is a strong, smooth cord that connects finger bones to muscles in the hand. Extensor tendons are located just under the skin, directly on the bone, on the back of the hand and fingers.
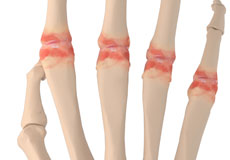
Metacarpophalangeal Joint Arthritis
The bones of the hand are called metacarpals and the bones of the fingers are called phalanges. The metacarpophalangeal joint or MP joint, also known as the first knuckle, is the large joint in the hand where the finger bones meet the hand bones.
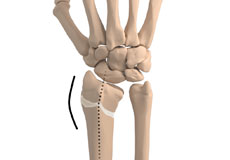
Malunion of a Fracture
Malunion of a fracture is a condition where the fractured ends of a bone heal in a misaligned position resulting in bone deformity. Malunions may occur in any bone fractures in the body often due to trauma.
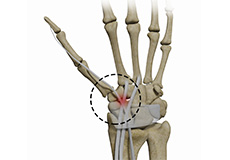
Distal Intersection Syndrome
Distal intersection syndrome also referred to as tenosynovitis of the radial wrist extensors is characterized by the radial wrist and forearm pain. Distal intersection syndrome is tenosynovitis of the third extensor compartment (extensor pollicis longus) where it crosses the second extensor compartment.

Wrist Arthroscopy
Wrist arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed to view, diagnose and treat problems of your wrist joint.
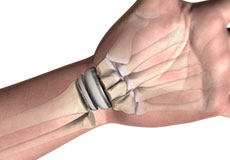
Wrist Joint Replacement
Wrist Joint Replacement is a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed to view, diagnose and treat problems of your wrist joint.
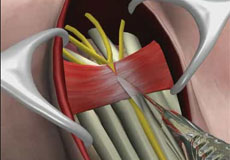
Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
The common symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome include numbness and tingling sensation in all the fingers except the little finger, pain and burning sensation in your hand and wrist that may radiate up the arm and elbow, and weakness in hand with diminished grip strength.
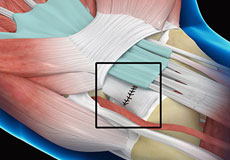
Wrist Ligament Reconstruction
Surgical treatment in the form of wrist ligament reconstruction may be indicated in cases where the wrist ligament is completely torn. The ligament will usually need to be reconstructed when ligament damage is noted after a period of 6 months or more after the initial injury.
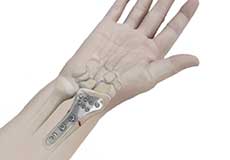
Wrist Open Reduction and Internal Fixation
Open reduction and internal fixation of the wrist is a surgical technique employed for the treatment of severe wrist fractures to restore normal anatomy and improve range of motion and function.
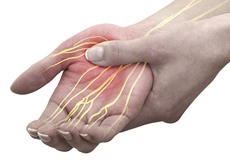
Peripheral Nerve Repair
The peripheral nerves are the nerve fibers that compose the area from head to toe, connecting the brain and spinal cord with the rest of the body parts. Nerves transmit electrical impulses and signals to and from the brain.
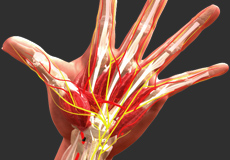
Microvascular Surgery
Microvascular surgery or microsurgery is a surgical technique for joining or repairing the damaged blood vessels and nerves during reconstructive surgery of body parts. Reconstructive surgery restores the functioning of the body parts by improving circulation.
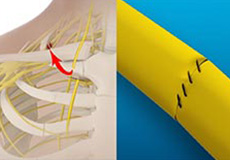
Nerve Transfers
A nerve transfer is a surgical procedure in which a portion of a healthy nerve is transferred to the site of a damaged nerve. This procedure is performed to restore normal function at the injured site.
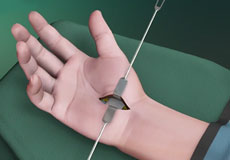
Hand Fracture Surgery
A hand fracture is a break in one of the bones in the hand, which occurs when force greater than the bearable limit is applied against a bone.
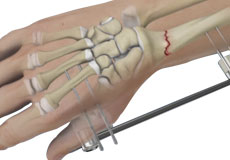
Wrist Fracture Fixation
Wrist fractures are breaks in any of the bones that form your wrist joint. Your wrist is made up of 8 small bones present in your hand and the adjacent ends of the 2 long bones of the forearm.
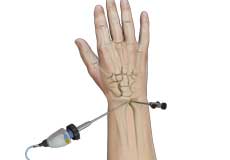
Distal Radioulnar Joint Arthroscopy
The distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) is a pivot type synovial joint located between the radius and the ulna just proximal to the wrist joint and assists in pronation and supination of the forearm.
Sports Injury Management of Hand, Wrist and Elbow
Sports injuries are injuries that most commonly occur during sports and exercises. These injuries may result from accidents, poor training practices, and use of improper protective gear, lack of conditioning, and insufficient warm-up and stretching.
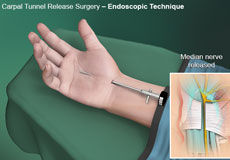
Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Surgery
Carpal tunnel can be treated with conservative measures or surgical intervention. Conservative treatment options may include treating any underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes and arthritis.
Microsurgical Flap Procedure of the Hand
A microsurgical flap procedure of the hand is a surgery performed to cover a defect in an injured hand using skin along with the underlying healthy tissue of varying thickness harvested from adjacent tissue or another part of the body.
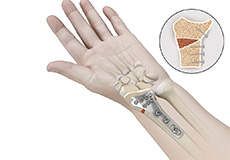
Osteotomy for Distal Radius Malunion
Osteotomy is a surgical procedure to cut and reshape deformed bones. Your doctor recommends osteotomy to correct distal radius malunion when non-surgical options such as splinting or physical therapy are unsuccessful.
